Media elements used in this module are protected by a variety of copyright licenses. Please use the "copyright terms" link associated with each item below for more information.
Click an image to view it at full size in a new browser window/tab.

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / J. D. Griggs
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Eruption of Kilauea Volcano beginning in 1983. Arching lava fountain - bright red lava is arching from the side of a slope and to the right.
|
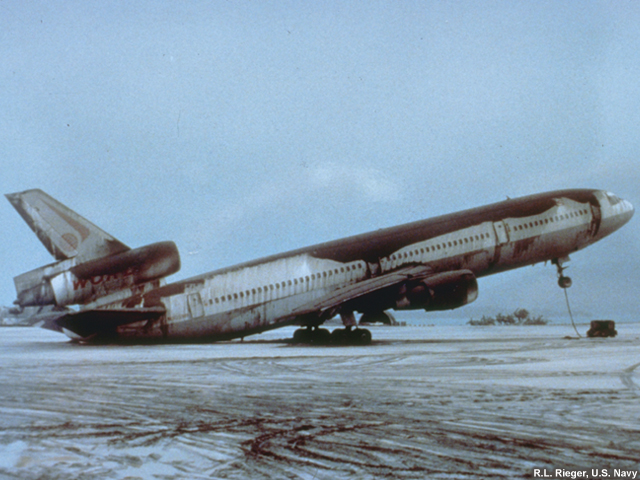

credits:
R.L. Rieger, U.S. Navy
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Ashfall on a commercial airplane in the Phillipines after the eruption of Mt. Pinatubo. So much ash is on the airplane that the tail has tipped to ground.
|

credits:
Creative Commons macha.cl
copyright terms:
Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0
description:
Houses buried in volcanic ash up to their first-floor windows in a town near the Chaiten volcano. The volcano plume is in the background.
|
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / Bobbie Myers and Carolyn Driedger
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
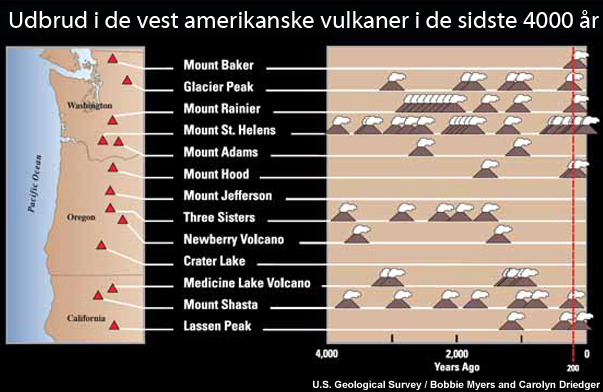
During the past 4,000 years eruptions have occurred at an average rate of about 2 per century. This chart shows 13 volcanoes on a map of Washington, Oregon, and northern California and time lines for each showing the ages of their eruptions.
|
|
|
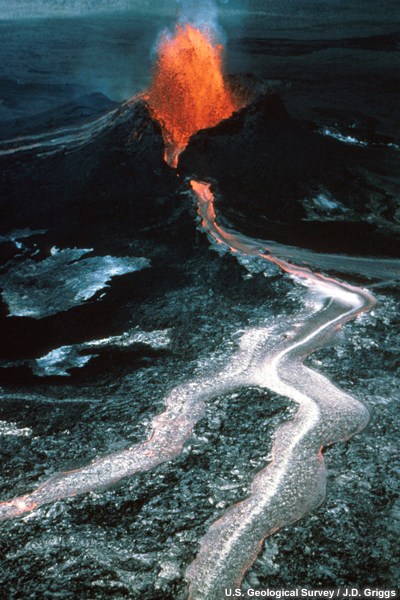

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / J.D. Griggs
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Fountaining and lava flow from Pu'u O'o.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / J. D. Griggs
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Braided lava flows spread from a lava fountain on the side of Pu`u `O`o cone.
|
credits:
The COMET Program / USGS
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
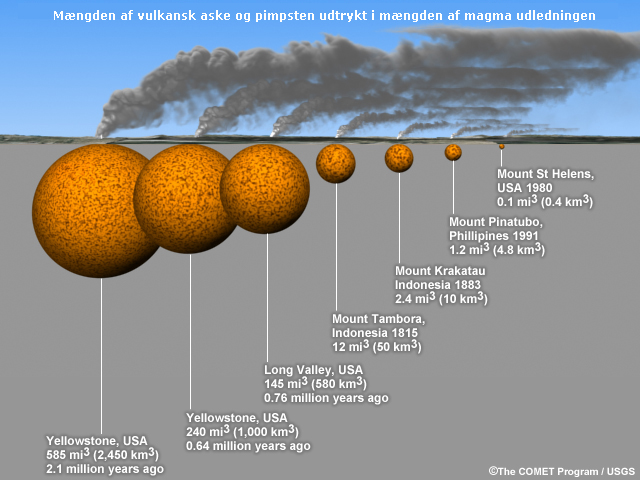
A chart showing the relative sizes of 7 eruptions: Yellowstone is the biggest, Mt St Helens is the smallest in terms of volume of material expelled to the surface.
|
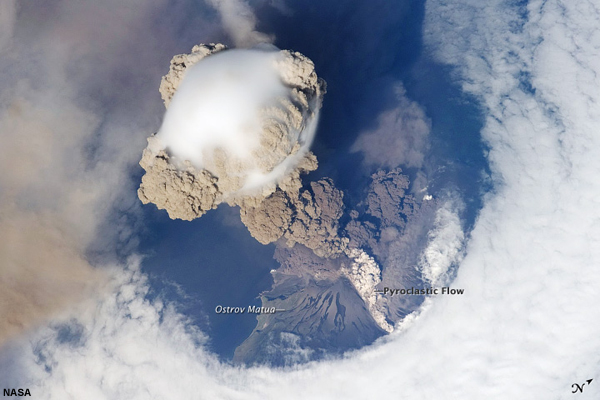

credits:
NASA
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
This is a view from space of the eruption of Sarychev volcano. The plume appears to be a combination of brown ash and white steam. The vigorously rising plume gives the steam a bubble-like appearance.
|
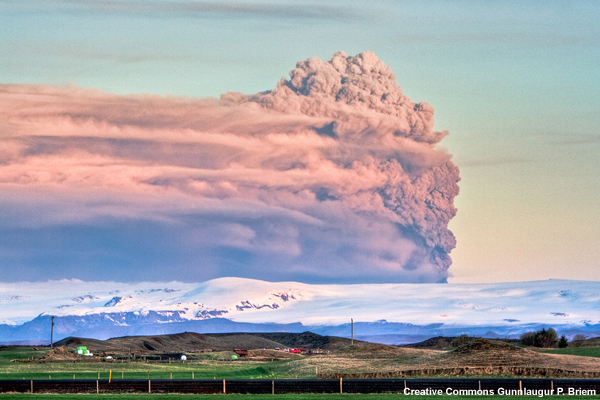

credits:
Creative Commons Gunnlaugur P. Briem
copyright terms:
Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0
description:
Dark-grey ash plume rises high above Iceland, in this early morning photo of Eyjafjalljokull' s eruption.
|
|
|
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
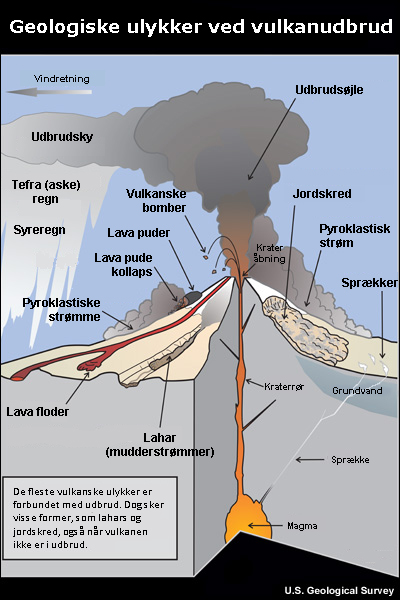
A graphic showing hazards associated with volcanic eruptions. 11 hazards are shown:lava flow, pyroclastic flow, lahar, lava dome collapse, tephra, eruption column, eruption cloud, acid rain, bombs, landslide, fumaroles.
|
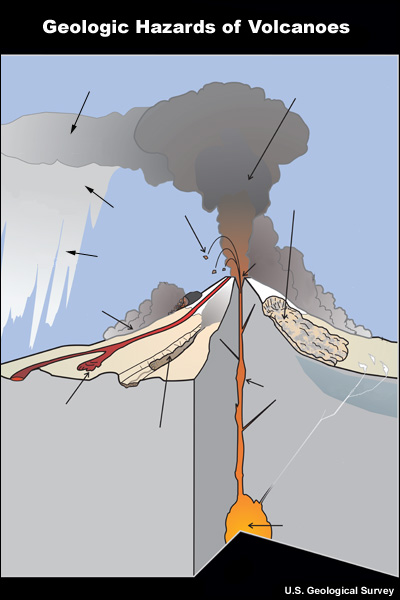
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A graphic showing hazards associated with volcanic eruptions. 11 hazards are shown:lava flow, pyroclastic flow, lahar, lava dome collapse, tephra, eruption column, eruption cloud, acid rain, bombs, landslide, fumaroles.
|
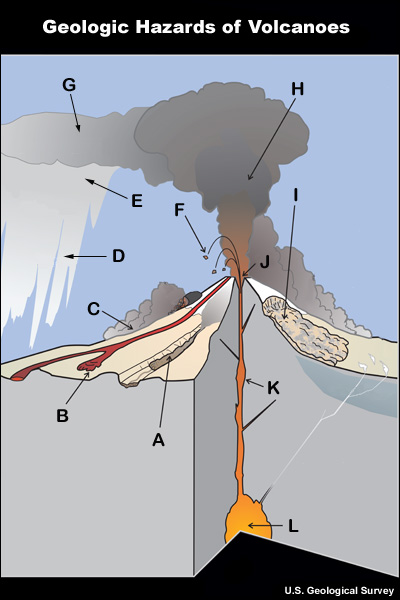
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A graphic showing hazards associated with volcanic eruptions. 11 hazards are shown:lava flow, pyroclastic flow, lahar, lava dome collapse, tephra, eruption column, eruption cloud, acid rain, bombs, landslide, fissures.
|
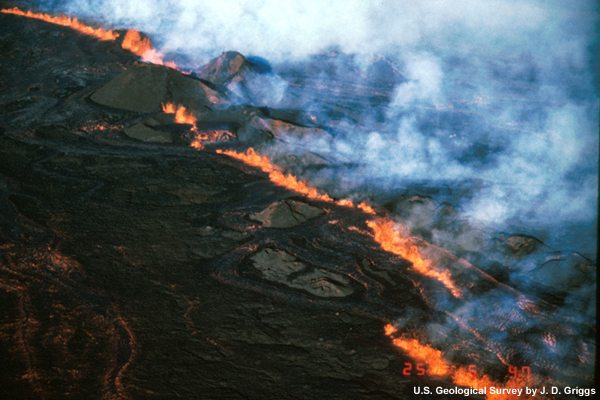

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / J. D. Griggs
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Magma fountaining at fissures during the 1984 eruption of Mauna Loa Volcano.
|
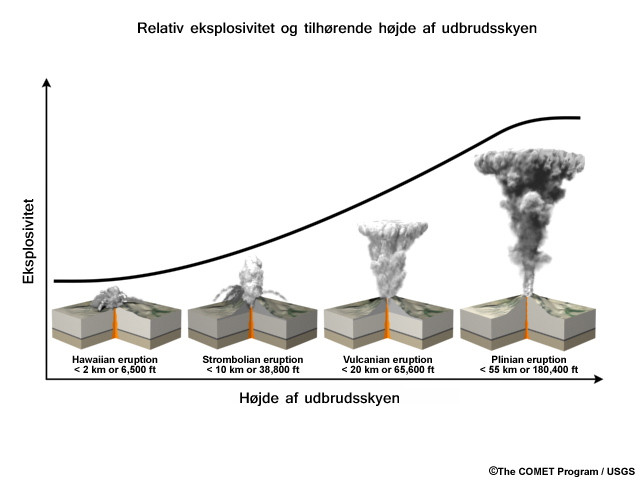
credits:
The COMET Program / USGS
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Graphic compares the height of an eruption column (ash plume) in ft/km to its explosiveness; that is, the more explosive an eruption, the higher the ash/water and aerosols are ejected into the atmosphere.
|
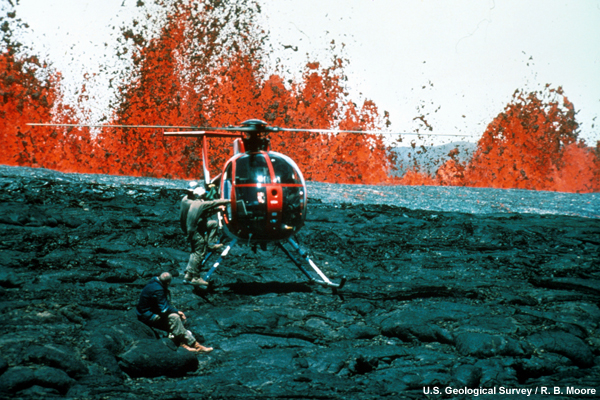

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / R. B. Moore
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Hawaiian Volcano Observatory geologists at lava fountains. Helicopters provided access to remote areas of the eruption and were essential for safety. The lava fountain is rising near the helicopter.
|
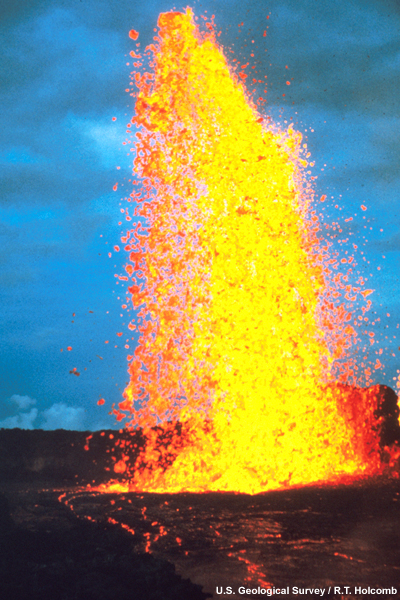

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / R.T. Holcomb
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Mauna Ulu fountain, viewed from the north rim. Similar to a fountain of foam where the base is solid and the top of the fountain breaks up into smaller chunks.
|
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Mount St. Helens 1980 explosive eruption with voluminous plume of tephra.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / Peter W. Lipman
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A pyroclastic flow from the August 7, 1980 eruption stretches from Mount St. Helens' crater to the valley floor below.
|
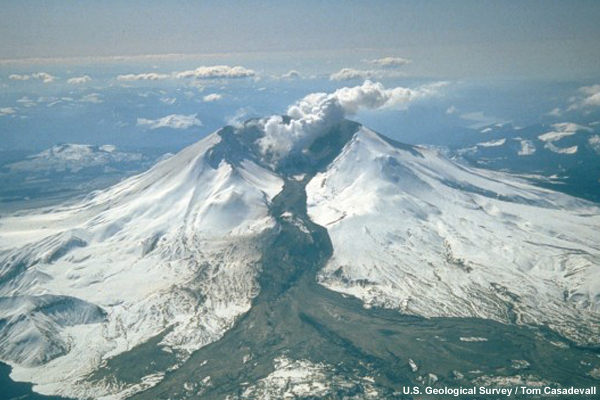

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / Tom Casadevall
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A lahar (the dark deposit on the snow) flowing from the crater of Mt St Helens into the North Fork Toutle River valley.
|
|
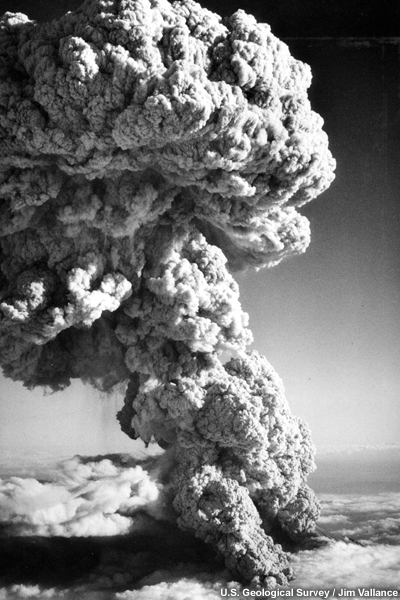

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / Jim Vallance
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Third pulse of Mount St. Helens eruption of July 22. Aerial view taken at 1907 PDT looking south, showing spreading mushroom top on convectively rising column and cloud of ash rising from an ash flow that has swept northward out of volcano's crater amphitheater. North west slope of volcano no visible at lower right. Column height about 15 km.
|
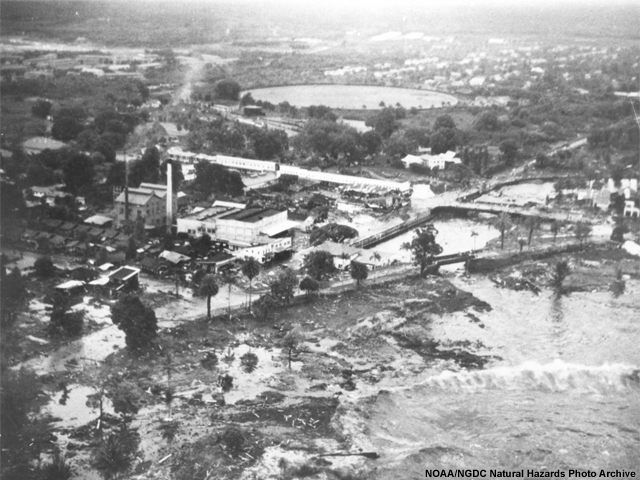

credits:
NOAA/NGDC Natural Hazards Photo Archive
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Hilo, Hawaii. Aerial view showing extent of innudation in area of Hilo Electric Company resulting from first wave as secondary wave approaches the area.
|
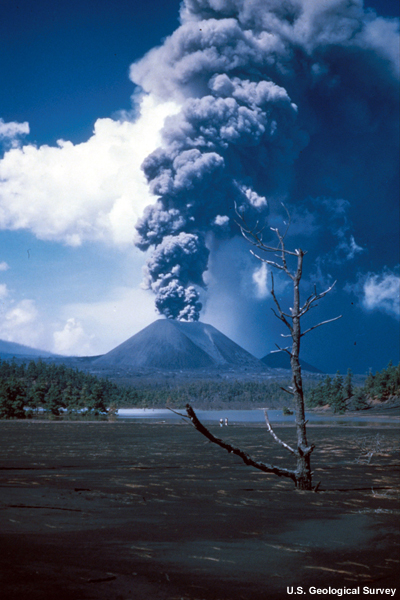

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A volcanic plume rises high above Mt. Paricutin, Mexico.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / J. D. Griggs
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Geologist measuring the height of a lava fountain.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Ash from Mt. Pinatubo's eruption covers many buildings and a hospital in the foreground. The sky is grey with ash, all greenery is covered in grey too.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Space Shuttle photograph of the Earth over South America taken on August 8, 1991, showing double layer of Pinatubo aerosol cloud (dark streaks) above high cumulonimbus tops
|
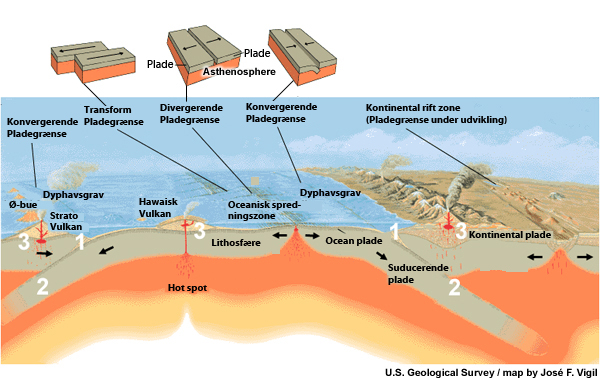
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / map by José F. Vigil
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A cross-section illustrating the main type of plate boundaries - convergent, divergent, transform and their likely physical manifestations.
|
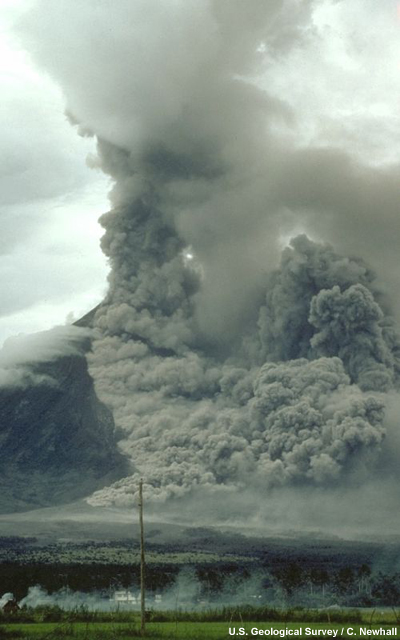

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / C. Newhall
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Pyroclastic flow sweeps down the side of Mayon Volcano, Philippines. Note the ground-hugging cloud of ash (lower left) that is billowing from the pyroclastic flow and the eruption column rising from the top of the volcano.
|
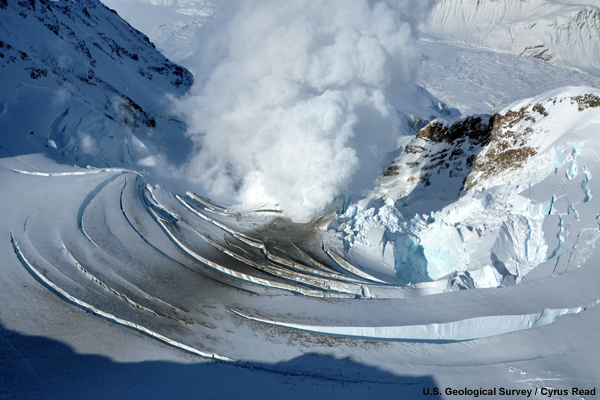

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / Cyrus Read
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
The glacier that filled the crater of Mt. Redoubt is collapsing because of the increased temperature underneath. This photo was taken on March 21, 2009, the day before Redoubt first erupted.
|
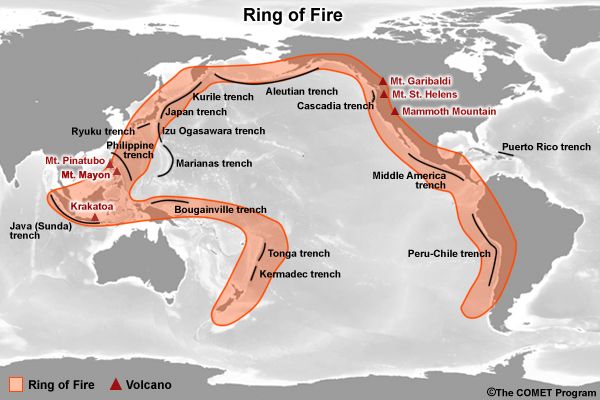
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Volcanic arcs and oceanic trenches partly encircling the Pacific Basin form the so-called Ring of Fire, a zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The trenches are shown in blue-green. The volcanic island arcs, although not labelled, are parallel to, and always landward of, the trenches.
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / A.M. Sarna-Wojcicki
copyright terms:
Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic
description:
Close view of a single ash particle from the eruption of Mount St. Helens; image is from a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The tiny voids or holes are called vesicles and were created by expanding gas bubbles during the eruption of magma. (USGS description)
|
pop a window to view .swf file
credits:
NASA
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
International Space Station view of Sarychev Volcano (Kuril Islands, northeast of Japan) in an early stage of eruption on June 12, 2009. The ash plume is viewed from above and it has pierced the cloud cover above the volcano. A pyroclastic flow is visible on the volcano's flank.
|
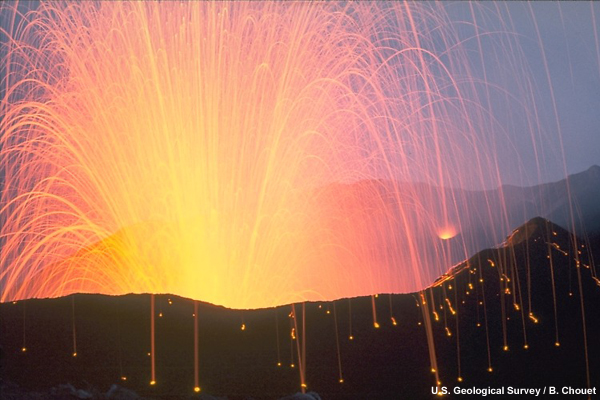

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / B. Chouet
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Close view of Stromboli Volcano erupting incandescent molten lava fragments.
|
|
|

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / D. Wieprecht
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Different types of tephra are compared against the size of a US penny.
|
|
|
|
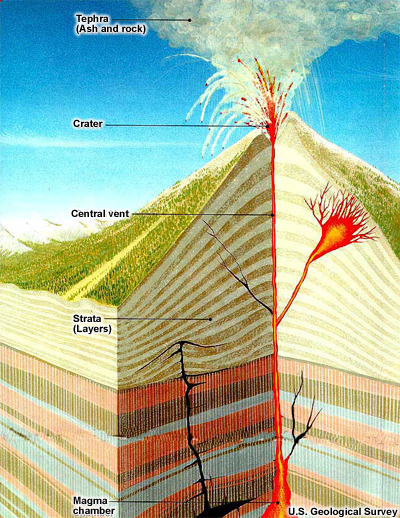
credits:
U.S. Geological Survey
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
A cross-section of a typical volcano during an eruption. Starting at the magma chamber, magma rises through strata (rock layers) to the surface, following one or more conduits. While most magma rises to the top of the volcano and erupts through the central vent, other magma may follow diverging conduits and erupt on the flanks of the volcano. Some magma may never reach the surface, intruding laterally into the strata instead.
|
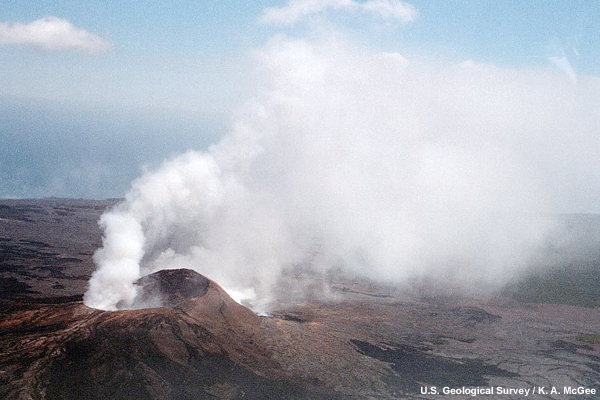

credits:
U.S. Geological Survey / K. A. McGee
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
Sulfur dioxide and other volcanic gases rise from the Pu`u `O`o vent on Kilauea Volcano, Hawai`i
|
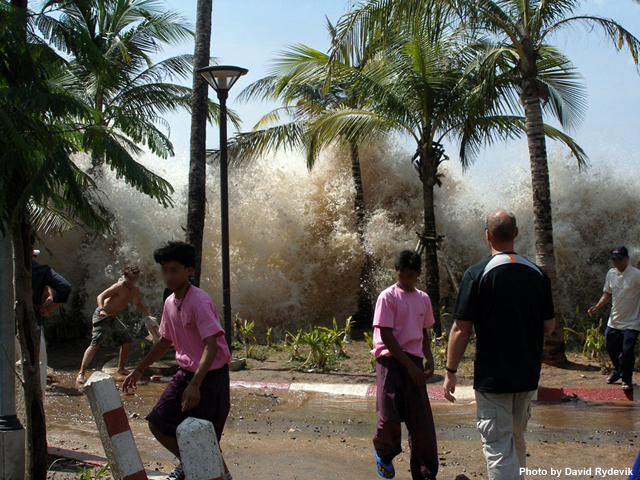

credits:
Photo by David Rydevik
copyright terms:
COMET Standard Terms of Use
description:
The first wave of the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami hits Ao Nang, Thailand.
|